Risk Management
We understand risk as the effect of uncertainty on the achievement of the Company's objectives, considering the effect as a positive or negative deviation, or both (threats and opportunities) from what is expected.
Integrated risk management is framed within the Integrated Risk Management System, based on the ISO 31000 standard, COSO ERM, Good Governance Code, Code of Conduct, Comprehensive Risk Policy and Best Practices Compendium, among others. Having an integrated risk management, with the active participation of senior management, allows the Company and its subsidiaries and affiliates to adequately support risk-based decision making, using a common language and tools to act in a timely and effective manner in the face of uncertainty associated with objective achievement.
| 
|
Risk management activities must be carried out at least once a year to identify and assess strategic risks, inherent risks of major impact -RIMI and process or operational risks (including human rights risks - HR, social - SS, environmental - AMB, climate change, fraud-asset misappropriation and personal data protection (PDP), among others). The activities performed as part of the risk management cycle are reported to the Board of Directors through the Strategy, Governance and Risk Committee, which is held at least twice a year.
In order to strengthen the control environment and risk culture in the organization, Promigas has implemented the three lines model.
1. First Line
The first line of defense is constituted by each of the areas or collaborators within the companies that manage the business, they are the owners of processes, called risk managers. This means that those who make up this line of defense have the following functions:
- Responsible in the first measure to identify, evaluate, manage, monitor and report the risks associated with their processes.
- Evaluate the sufficiency of the controls implemented to contain the risks of your process.
- Identify, remediate and report gaps in risk limits.
- Report to the 2nd line of defense the changes presented in the risks and controls associated with their processes.
- Work with the support of the 2nd line of defense to remedy identified gaps.
- Maintain the current risk matrices in accordance with the changes presented in their processes.
2.Second Line
This line of defense is made up of the Risk and Compliance Management or equivalent risk areas in each company, in charge of such functions, which must continuously monitor compliance with all Risk obligations:
- Establish a corporate risk management framework commensurate with the size, profile and complexity of the organization's operations.
- Methodologically support the frontline in the identification and management of their risks.
- Monitor that risk levels are consistent with appetite, policy and regulatory requirements.
- Establish the appropriate governance required to ensure that the front line owns the risks.
- Present the risk profile of the organization and the risk management carried out to Senior Management and Board of Directors.
3. Third Line
The third line of defense plays an important role in independently assessing the company's risk management and controls, as well as the processes and systems they under, reporting to the Audit Committee. The persons in charge of internal audits who must perform these reviews must be competent and properly trained and not involved in the development, implementation and operation of the risk/control structure. This review may be conducted by audit staff or by personnel independent of the process or system being examined, but may also involve appropriately qualified external actors. The functions of this line are:
- Prepare the annual audit plan and strictly comply with it.
-
Carry out a detailed evaluation of the effectiveness and adequacy of the SCI, in the processes of the organization that are relevant.
-
Review the procedures adopted by management to ensure compliance with legal and regulatory requirements, internal codes and the implementation of policies and procedures.
-
Follow up on the implementation of the action plans established by the organization.
The second line, which includes Promigas' Risk and Compliance Management, establishes the guidelines and methodology, monitoring, implementation and ongoing support.
Promigas Integrated Risk Management Responsibility Framework 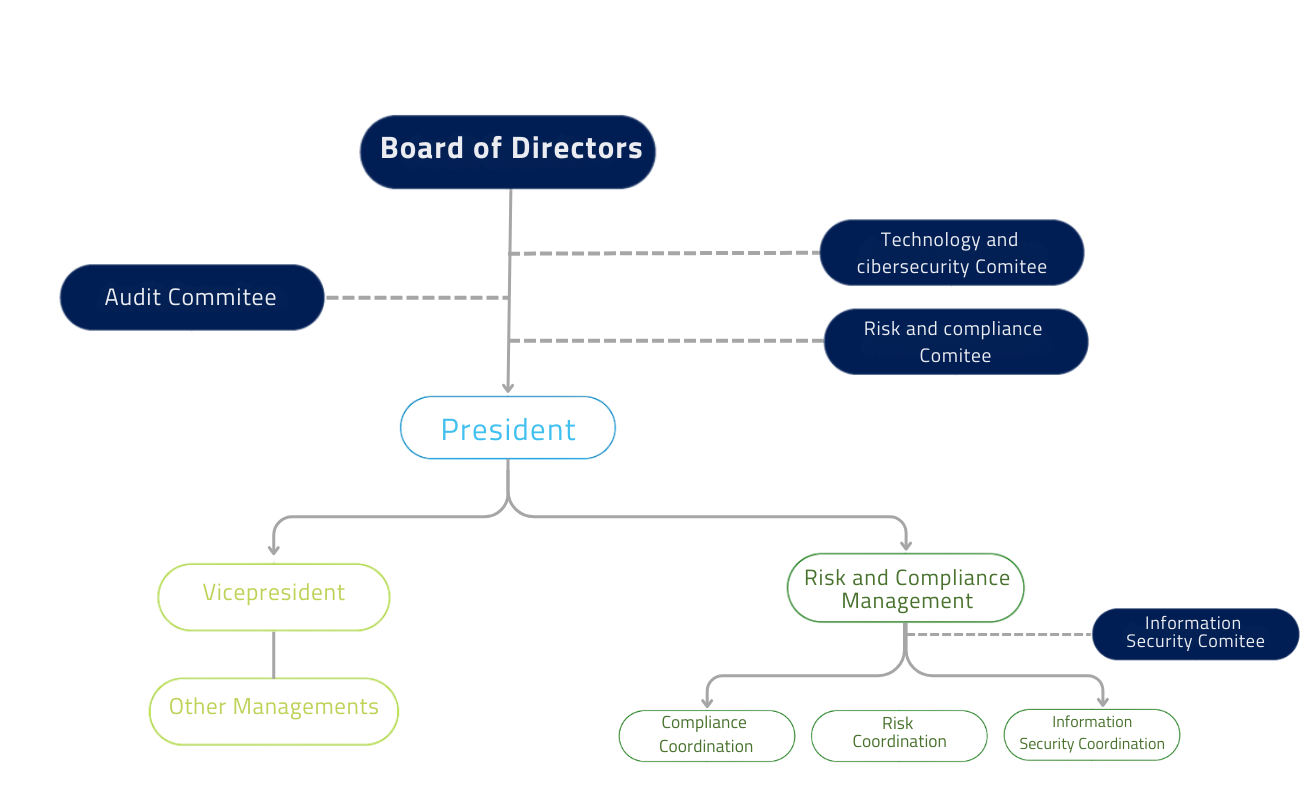
The second line at Promigas defines Risk Management as a driver of the strategy, mainly from four dimensions: compliance, business risks, information security and risks associated with the issuance of Financial Statements. Responsibilities for risk, control and supervision are clearly assigned through the model based on an adequate segregation of duties.
At Promigas, after the President, the Risk and Compliance Manager has the highest seniority, and the responsibility for operational risk management. They report on risk management to the President of the Company and the Strategy, Governance and Risk Committee.
The methodology defined to monitor and keep the system updated is based on the following five-step cycle, it applies to all types of strategic and tactical risks that are managed in the organization:
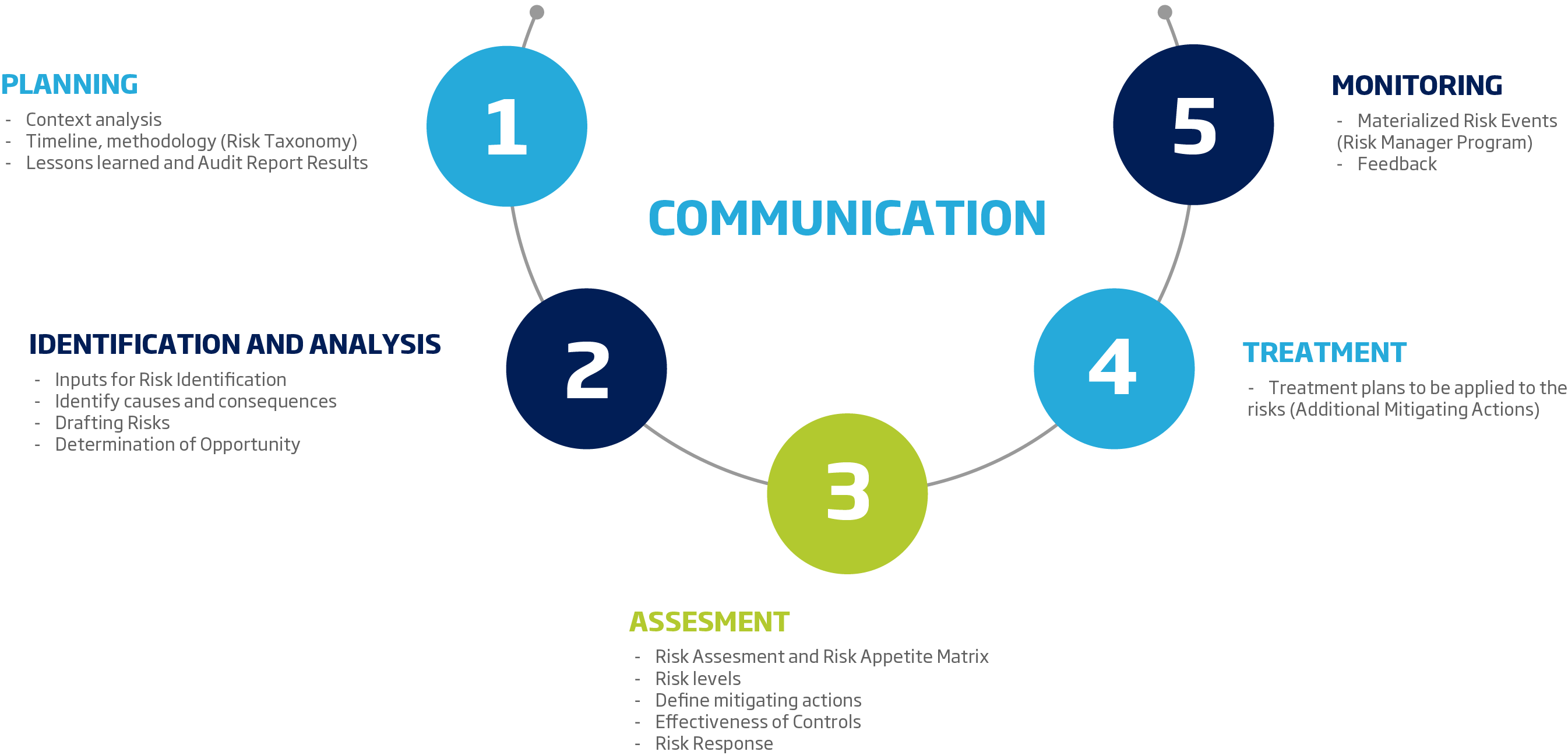
1. Plan: It begins with a context analysis through which the external and internal factors relevant to the achievement of the objectives or that may affect the results proposed by the organization are determined.
2. Identification and Analysis: It includes the phases of identification, analysis and assessment of risk and allows to have a clear horizon on business or process risks, for which the areas must be clear about the context of their processes and the main activities that are aimed at achieving the objectives of the business.
Once the risks have been identified, an initial assessment is carried out to identify the inherent risk profile, without taking into account the existence of all the associated mitigation controls, and then a residual assessment is carried out taking into account the implementation of these.
3. Treat: For strategic risks, senior management defines action plans for those that according to their residual assessment are at the extreme and high risk level. For process or operational risks, the feasibility of implementing additional mitigants depending on the nature of the risk is reviewed with process leaders.
4. Monitor: Monitoring of controls associated with both qualified business risks at high and extreme levels, as well as those associated with inherent risks of greater impact and strategic risks. This activity allows to evaluate the control in terms of its solidity, by validating that they have an adequate structure and that they are executed according to their design.
The results are reported to the Presidency, and to the Risk and Compliance Committee, in the case of the results of RIMI and Strategic monitoring, these are presented to the Board of Directors.
5. Communicate: This last stage is considered transversal, since it allows a successful follow-up to each of the previous ones.
The Integral Risk Management is worked under the reference framework based on the best practices ISO 31000: 2018, COSO III and Dow Jones Sustainability Index – DJSI.
Managing risks and opportunities with an integrated view
Within the Risk and Opportunity Management, it was possible to identify each of them, according to the definition of three major categories of risks, which are:
1. Emerging Strategic: New or emerging risks from local or international conditions, situations or trends that could significantly affect the financial strength, competitive position or reputation of the company or sector. Additionally, they have low frequency, high impact, high degree of uncertainty and a difficulty in quantifying them due to the absence of data.
2. Key Strategic: These are those that directly affect the fulfillment of the Strategic Business Objectives and the Missionary Processes of the Organization.
3. Inherent risk of greater impact (RIMI): Level of risk specific to the business, without taking into account the effect of controls, which affects the Core business, strategic objectives, business continuity and high reputational impact, and is located at the extreme level of the risk map.
From a vision of integrated thinking, we connect key risks with capital, material issues, their mitigating factors and the work carried out in 2023, taking into account economic, governance, social and environmental aspects, which are drivers for value creation and continuous improvement.
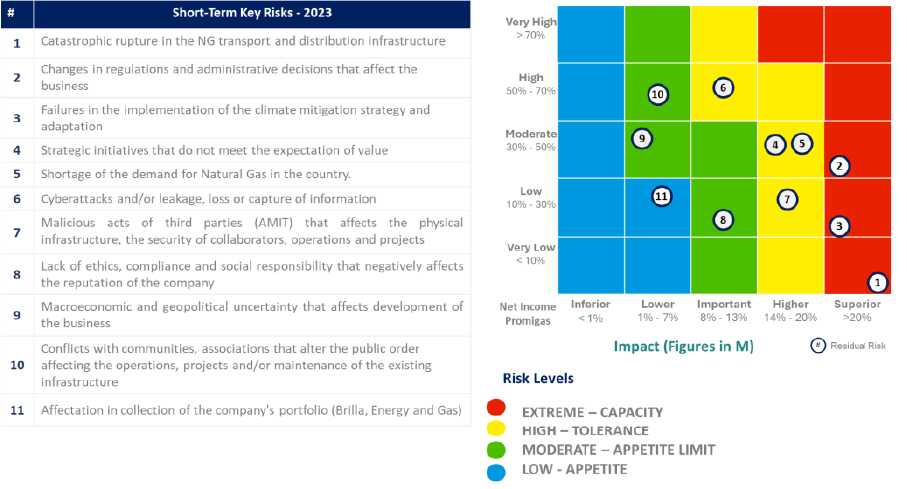
No.
|
Risks
|
Material Issues
|
Capital
|
Mitigating
|
Management 2023
|
1
|
Catastrophic rupture of NG transportation and distribution infrastructure.
|
Service quality
Process safety
Environmental performance |
Industrial natural
|
Pipeline integrity risk analysis.
Follow-up on compliance with the maintenance plan.
High consequence area (HCA) inspection.
Fitness-for-purpose study based on ILI (inline inspection).
Inspection and marking of the right-of-way.
|
The mechanical protection plate project continues.
Intelligent ILI inspection was performed.
The implementation of Phase III of the AVR Project 'Hazard, vulnerability and geotechnical risk' continues.
|
2
|
Changes in rules and regulations affecting the business
|
Financial performance
New business
|
Financial
| | -
Ongoing monitoring of procedures and timely compliance with CREG requirements. Stage I of the tariff methodology was implemented.
|
3
|
Failures in the implementation of the climate mitigation and adaptation strategy.
|
Environmental performance Financial performance
|
Natural
Industrial
Financial
|
Pipeline integrity risk analysis.
Follow-up on the execution of the activities associated with the high priority equipment defined in the maintenance plan.
Monitoring and tracking of banks and slopes through bathymetry and topography.
| |
4
|
Strategic initiatives that do not meet value expectations.
|
Service quality
HT development and
well-being
|
Human
Intellectual
Financial
| | -
A complementary portfolio of Carbon Management and energy efficiency solutions was designed.
|
5
|
Natural Gas shortage in the country.
|
Financial performance
New business
|
Industrial Natural
|
Market monitoring, definition and approval of commercial strategies.
Monitoring of gas supply to customers.
Management of flow variables with molecule producers.
Review of available capacities.
| -
Sector working groups and gas supplies from potential discoveries (Arrecife, Hocol, Magic, among others).
|
6
|
Cyber-attacks or leakage, loss or capture of information.
|
Service quality Process safety
|
Social and Relational Intellectual
|
Data Loss Prevention (DLP).
Periodic review of vulnerabilities in the IT infrastructure.
Automatic restriction of access to critical options in applications under SOX scope.
Timely removal of user access to systems.
| -
Implementation of cybersecurity initiatives with scope to the IT environment and the different businesses established in the short term.
|
7
|
Malicious acts by third parties (AMIT, for its acronym in Spanish), which affect the physical infrastructure, employee safety, operations and projects.
|
Service quality
Financial performance
|
Social and relational Financial
|
Monitoring of the national, regional and local context in Colombia and Peru.
Monitoring of public disturbance events in areas of operation and interest that may affect the business.
Follow-up of infrastructure and facilities safety studies.
| -
Incident and crisis management protocols were developed. The Crisis Management Manual has been updated.
|
8
|
Lack of ethics, compliance and social responsibility that negatively affects the companies’ reputation.
|
Financial performance Service quality
Contribution to social progress
|
Social and relational
Financial
|
Definition and approval of communication strategies.
Monitoring of media publications, and according to the situation that arises, follow-up is carried out.
| -
Monitoring and communications in the territories have been strengthened.
|
9
|
Macroeconomic and geopolitical uncertainty affecting business development.
|
Innovation
New business
|
Financial intellectual
| | -
The impacts of macroeconomic and geopolitical variables are monitored and analyzed.
|
10
|
Conflicts with communities and associations that disturb public order and affect operations, projects or maintenance of existing infrastructure.
|
Environmental Performance
New business
|
Social and relational
Industrial
Natural
|
Follow-up on the implementation of social management measures and community relations in the field for projects.
Analysis of the need for prior consultation before the modification of projects that are subject to environmental licensing.
Follow-up of compliance with the social strategy in the projects.
Monitoring of social and environmental issues in projects.
| -
A community characterization was conducted for La Guajira.
-
Incident and crisis management protocols were developed.
|
11
|
Negative effects on collection of the Company's portfolio (Brilla, Energía y Gas).
|
Financial performance
|
Financial
| -
Monitoring of collection and portfolio indicators for gas and Brilla.
-
Refinancing plans tailored to the client's needs.
-
Brilla Portfolio Committee funded by Promigas.
| -
Loyalty plans have been strengthened to be closer to customers and improve their payment culture.
-
A score model based on advanced analytics was implemented, which allows us to recompose the offers and mitigate the impact of portfolio impairment.
|
The heat map shows the results of the strategic risks assessment according to the company's risk appetite:
Emerging Risks
Risks
|
Impact
|
Mitigating actions
|
1.Ecosystems and Basins degradation
Habitat degradation, decreased biodiversity and the disruption of natural cycles such as water and carbon are occurring at an accelerated pace due to human interventions. Likewise, the increasing impact on health and the functionality of natural environments and critical infrastructures make this problem a risk with potentially worrying impacts on the continuity of our business.
| -
Approval of stricter environmental regulations that could increase operating costs or generate operational restrictions.
-
New environmental requirements and restrictions for the construction of infrastructure and for access to natural resources used by Promigas.
-
Damage to infrastructure due to destabilization of the soil and impact on communities neighboring the gas pipeline.
-
Additional demands from regulators and stakeholders to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and protect ecosystems.
| -
Continue planning and implementing conservation and restoration activities for ecosystems and watersheds in the area of influence of the projects and operational and maintenance activities.
-
Promote the research, development and implementation of sustainable technologies to mitigate the impacts of ecosystems and watersheds in the area of influence of the projects and operational and maintenance activities.
-
Construction, operation and maintenance activities.
-
Promote the participation of communities neighbouring the gas pipeline through the Promigas Foundation in initiatives related to the protection of ecosystems, biodiversity and climate change mitigation.
|
Risk Management Process Audit
Internal and External audits are carried out annually. The criteria followed is ISO 9001:2015, ISO 14001:2015 and ISO 45001:2018, which provides the guidelines and standards to conduct the audit. In 2023, the internal audit conducted in Promigas with the general objective of evaluating and verifying the organization’s integrated management system, reported Risk Management as one of the strong and favorable aspects in place.
During the first semester of 2024, an external audit was conducted by Icontec with the same objective, identifying that the risk portfolio has been expanded to Strategic Risks, RIMI, ERM TPRM/TPI, Projects, Climate change, Operational fraud, Human rights – environmental, social and PDP. Regarding climate change, the organization implemented the methodological framework based on TCFD standard, the IPCC methodology, among others. As a result, the company defined the climate scenarios and horizons, 12 physical risks were identified for the entire corporate portafolio.
To address these physical risks that challenge our infrastructure, Promigas is developing several projects and actions with the purpose of adapting and reducing the impacts that may arise, such as early warnings, construction plans for works and variants, and adaptation plans for strategic assets.
Risk Culture
In the year 2023, at Promigas, we conducted a training program aimed at members of our Board of Directors, our management team and our employees focusing on fundamental issues such as the Transparency Law, business ethics, and the prevention of money laundering. This effort reflects our unwavering commitment to the highest ethical standards in all our interactions with various stakeholder groups, as well as compliance with current laws and regulations.
Through enriching activities like this, members of our board, management team and employees had the opportunity to delve deeper into their understanding of the risks they face in their respective roles. They also explored the vital importance of traceability in promoting transparency and accountability. The training covered a wide spectrum of regulations, both at the national and international levels, enabling our leaders to gain a comprehensive and up-to-date perspective on the responsibilities associated with their roles as members of the Board of Directors, and other key positions within our company.
Every new employee must enroll the induction course about our methodology in risk management. On the other hand, we organize at least two (2) risk corporative event whose main goal is to raise awareness among employees in the effective risk management. In addition, we prepare an annual training for all employees (including Promigas and its portfolio companies). This training is focused on the principles and changes in the risk management methodology.
Every new project must be evaluated by our risk methodology. In this process we consider the possible financial and climate impact, among others. In addition, when the organization is going to build or modify a natural gas infrastructure, those activities must be evaluated incorporating the hazard and operability study – HAZOP.
Supplier Risk Assessment
We have a methodology to identify and manage Third Party Risks based on the requirements of best practices and global benchmarks of economic, social, reputational and environmental performance in the energy sector.
The objectives of the assessment of these risks are:
Carrying out a proactive and sustainable management with third parties.
Preparing for changing, global and volatile environments.
Minimizing losses.
Protecting the company’s operation.
As part of the methodology and aligned with the sustainability approach proposed in the organization, where several risk dimensions are evaluated for services and goods to be received from third parties, including those that are considered intermediaries or agents, thus promoting a comprehensive analysis of third parties. These dimensions are:
|
Risk Dimensions
| Country
| Financial
| Business continuity and resilience
| Reputational
| Information security
| Services concentration
| Regulatory
| Industrial safety
| Social
| Environmental
|
|
|
Once each dimension has been rated, an average rating is established and placed on an XY level, where X is the billing axis and Y is the level of risk. As a result of the assessment and their position on the cartesian plane, suppliers could be labeled as Routine, Relevant, Critical or Strategic Critical. Considering this label, action plan or monitoring actions should be defined.
The Third Party Risk assessment is performed on the total population of third parties with which a relationship has been established with amounts greater than 12 current minimum monthly salaries in Colombia per year, and also with those who provide services in which they act as intermediaries of the company before a public entity or a public official, excluding third parties that are considered low risk (for example, cafeteria services, purchase of tickets, public utilities, among others).
|
| 
|
The Third-Party Risk evaluation is performed before the beginning of the contractual relationship, whereby the second line provides the contract managers with recommendations, applicable when a moderate or high exposure to risks is observed in any of the aforementioned dimensions, with the purpose of defining controls to prevent the occurrence of such identified risks, as defined in the current procedure. In some cases, depending on the risk level in the case of anti-corruption, a more in-depth due diligence is performed to take the most appropriate decisions and measures; however, if the level of the third-party intermediary is HIGH, the relation must be approved by the Procurement Committee to ensure a higher risk analysis.
As a result,
899 suppliers were evaluated during the year, which were categorized as routine suppliers (86%) and relevant suppliers (14%), which are associated with low risk levels. There were no cases of critical or critical-strategic third parties.